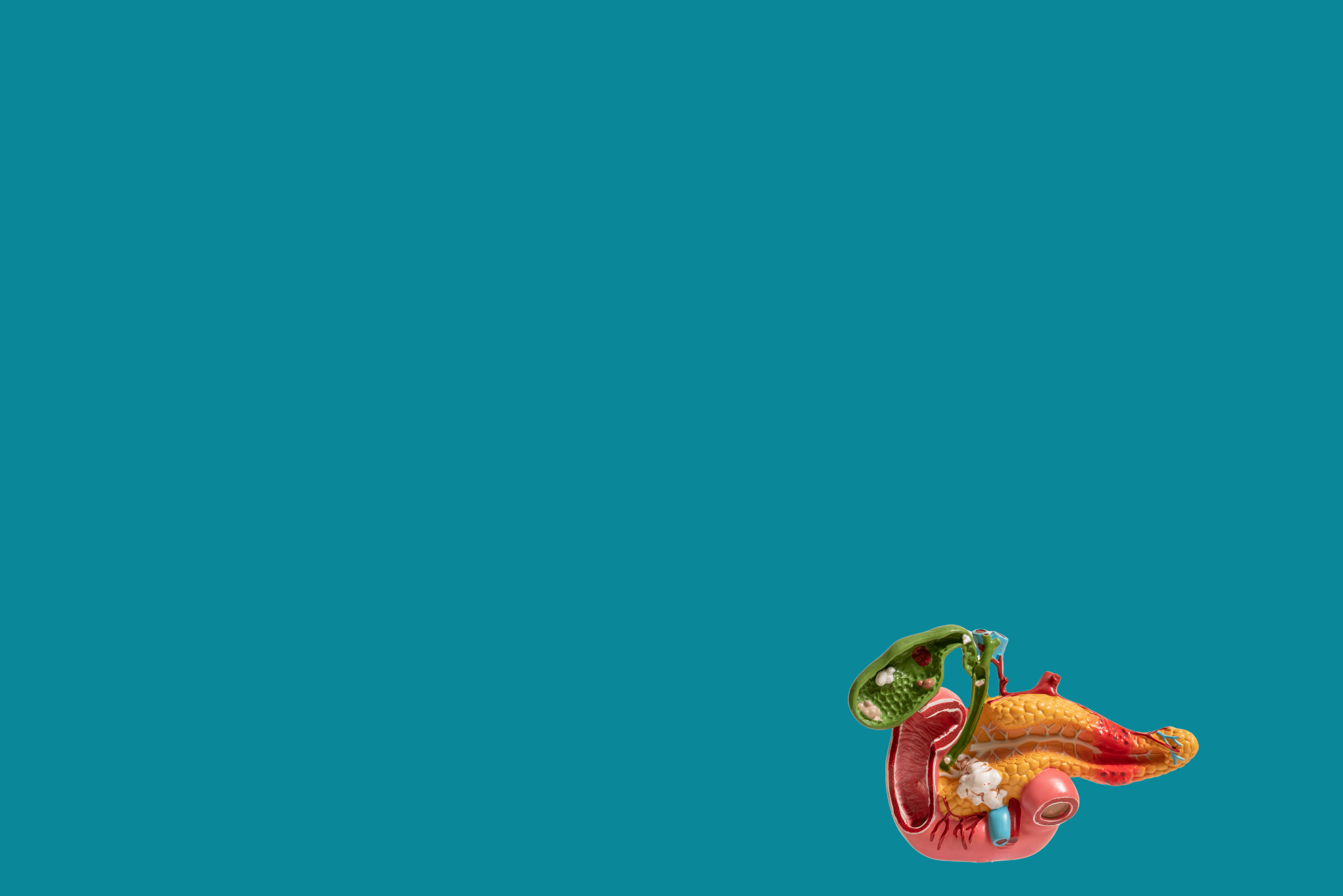overview
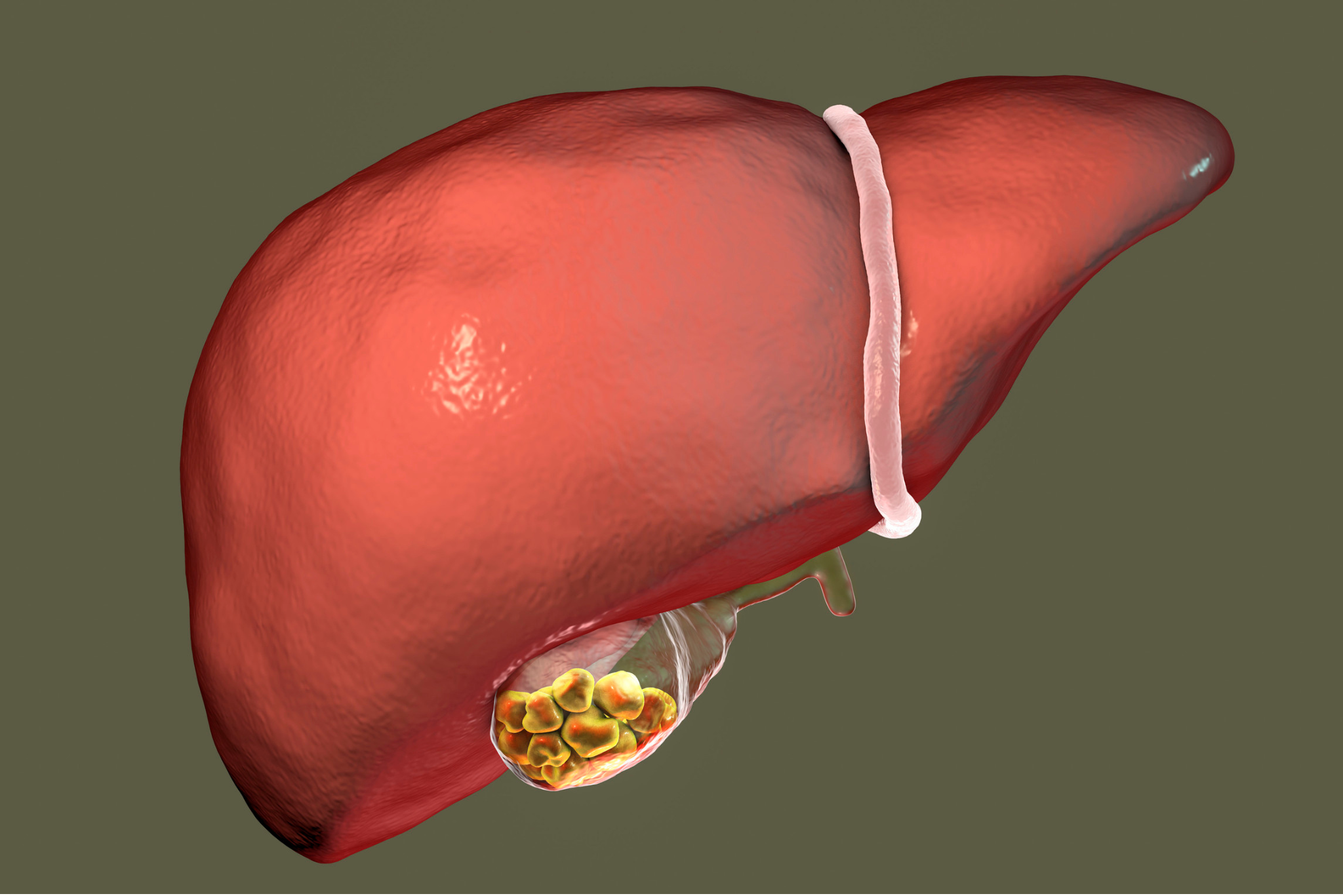
Gallbladder and bile duct problems are disorders that affect the system responsible for storing and transporting bile — a digestive fluid produced by the liver that helps break down fats. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under the liver. It stores and concentrates bile, releasing it into the bile ducts during digestion. When these organs or pathways become blocked, inflamed, or infected, it can lead to significant digestive and systemic issues.
One of the most common gallbladder problems is gallstones (cholelithiasis). These are solid particles that form in the gallbladder, often made of cholesterol or bilirubin. Gallstones can vary in size and may not always cause symptoms. However, when a gallstone blocks a bile duct, it can lead to intense abdominal pain, known as a gallbladder attack or biliary colic. Pain is typically felt in the upper right side of the abdomen and may radiate to the back or shoulder.
Symptoms & Diagnosis
The bile ducts can also develop problems. Choledocholithiasis occurs when gallstones move from the gallbladder into the common bile duct, causing obstruction. This can lead to jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, pale stools, and serious infections like cholangitis — a potentially life-threatening condition that involves inflammation and infection of the bile ducts. Symptoms may include high fever, chills, abdominal pain, and jaundice, and immediate treatment is required.
Another bile duct condition is biliary strictures, where the bile ducts become narrowed due to inflammation, injury (often from surgery), or scarring. This can restrict the flow of bile and lead to similar symptoms as a blockage. Rarely, tumors such as cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer) can form, typically presenting with jaundice, weight loss, and generalized fatigue.
Diagnosis of gallbladder and bile duct issues is typically done through imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, or specialized procedures like ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography), which can both diagnose and treat bile duct problems.Treatment depends on the severity and nature of the problem. Gallstones that cause symptoms often require surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy. Infections or blockages of the bile ducts may be treated with antibiotics, endoscopic procedures, or surgery. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet low in saturated fats, and avoiding rapid weight loss can help prevent gallbladder problems.
- Jaundice
- loss of appetite
- Fever
- Pain in right upper abdomen
- Loss of weight